What Is The Difference Between Hosting And CDN?
The Difference Between Hosting and Content Delivery Network
The traditional web hosting architecture has been crucial to the growth and success of the worldwide web over the last three decades. In the 1990s, several hosting companies emerged on the landscape. These companies rented massive servers in large data centers for hosting static files, which could then be accessed, viewed, and downloaded over the internet browser.
Users could enter the server IP or more conveniently with the emergence of Domain Name Service architecture – enter the website address into the browser. Needless to say, the internet completely changed the pre-existing business models and turned the competition landscape upside down. A startling fact is that 56% of the companies that were listed in the Forbes Fortune 500 company list of 2000 don’t exist anymore – they have been either acquired, merged, or been declared bankrupt.
With the emergence of new service and business models, as well as the transition of entire workloads to the internet, the simple and powerful client-server architecture has unfortunately been rendered obsolete today. When traffic increases beyond a ballpark, then the servers start to feel overloaded – as more response needs to be served – the processing engine starts to get cranked, and this negatively impacts the response time.
Consequently, viewers may experience aberrations such as slow loading speed, considerable time to render the page fully, constant buffering and latency if the viewer is watching a video over the internet. Moreover, today internet-based businesses typically see the entire globe as a target consumer base – the success of Amazon, Netflix, Uber reflects that.
However, under the simple client-server architecture model, when the user enters the request for a specific piece of content on the website or web app, then the request has to travel to the origin server and back. Because the origin server may be located tens of thousands of kilometers across the globe, the request to response time ( known technically as the round trip time) increases – adding additional latency to the website experience.
In modern competition, such aberrations in user experience can be a killer. Users have come to expect fast response time and TV-like experiences over the internet. When users get a sub-optimal experience in terms of loading and rendering on any website or web application, then they tend to churn very quickly.
It can directly translate into lost leads and lost sales for businesses, whose business model involves service delivery over the internet. In fact, according to an in-depth study by search engine giant, Google found that more than half of the users visiting a web page are likely to churn if it is taking more than 3 seconds to load. Google understands that page speed loading is a critical factor in user experience and in 2018 announced that page loading speed is going to be a vital ranking factor in its search engine indexing and ranking of web pages.
Other search engines such as Bing have made similar announcements, and it is clear now that to grab more eyeballs and stay on top of search results, which drives maximum traffic. But it is becoming even more challenging as websites are becoming more and more complex – Javascripts, videos, images, and multiple CSS – for enhanced user experience make the website complex, heavy and difficult to optimize for speed.
Because of these weaknesses within the traditional web hosting architecture, Content Delivery Networks have become extremely popular and widely adopted practice over the last decade. Content Delivery Networks, or CDNs for short, refers to a network of globally distributed and strategically located cache servers that cache the website content.
These cache servers dynamically store and update the website and web application content and are strategically distributed across the globe. Thus, when the user requests for a specific piece of content on the website or the web application, the request only needs to travel to the nearest cache server where the content is available. From this cache server, the response is served to the user.
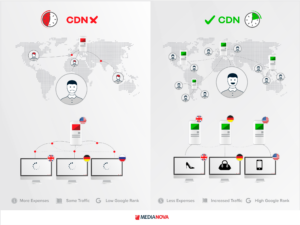
This CDN architecture decongests the network and reduces the load on the origin server. It also shortens the round trip time, because the response is served from the cache server that is in closest geographical proximity to the user.
Thus, we can summarize below the key differences between the traditional hosting and a CDN
- Traditional hosting is primarily concerned with the availability and accessibility of files – websites and web applications – over the internet. On the other hand, CDNs have emerged to solve the issue of improving the speed of access to these files over the internet
- Traditional hosting architecture provisions a single server – in shared or dedicated capacity – to deliver the assets. A major shortcoming with such an architecture arises when the user is located far away geographically from where the origin server is situated. Such an architecture, in such circumstances, can inevitably result in latency and unexpected buffering and delays.
- Another key advantage offered by a CDN over the traditional hosting architecture is that the load on the origin server gets reduced and distributed over the network of edge servers. This is good for the overall health, resilience and longevity of your server.
- By serving users located in different parts of the world, content from the closest web server, you are also increasing the efficiency by minimizing the packet loss and reducing the costs.
- A CDN offers excellent security against DDoS attacks – Distributed Denial of Service attacks – in which hackers overwhelm the website or application server with a massive number of requests in a very short time. The distributed nature of CDN network ensures that your origin server remains unaffected in case of a DDoS attack.
A CDN has become a prevalent solution, and businesses all around the world of all sizes are rapidly adopting it for improving their value chain and service delivery. According to Statista, the total data volume of global content delivery internet volume is projected to reach 254 exabytes per month, up from 54 exabytes per month in 2017.
Hence, investing in robust CDN infrastructure has become crucial for businesses to stay competitive and deliver top-notch content delivery experiences.
At Medianova, we are experts in providing you with world-class and cost-efficient CDN solutions to optimize and improve your site performance and content delivery. With our partnership; you are ready for online success. With years of expertise with experience in providing the right solution with our wide-range CDN solutions.